Muscle soreness is the result of strength training and it is a common element of the process in the beginning stages of muscle training. It signifies that your body is adapting to the new stimuli. In this article we will understand how to treat muscle soreness.
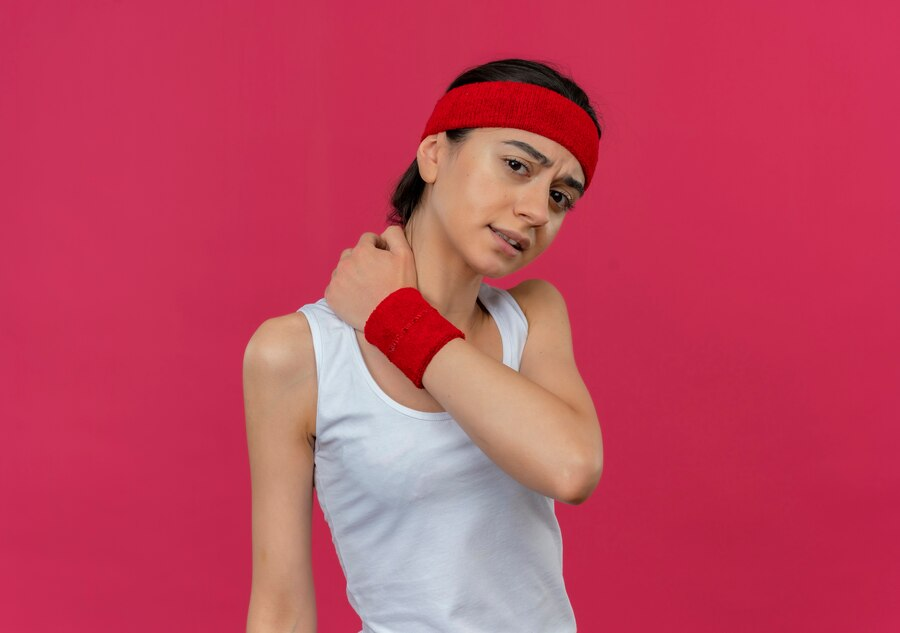

Muscle soreness or delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), as known scientifically, is a condition which arises 24-72 hours after exercise. You can experience muscle soreness in the form of mild discomfort or significant pain. You might feel uncomfortable in the beginning and soreness could also hinder your consistency of working out.
Reason for muscle soreness
Muscle soreness due to exercise is caused because of microscopic damage. The damage to your muscle tissues triggers an inflammatory response as the body begins to repair the tissues and grow back stronger. This is the reason for muscle soreness and stiffness. There are some factors that lead to muscle soreness:
Eccentric exercise:
Eccentric exercises which involve exercises like downhill running or lowering weight causes muscle damage and more soreness. These exercises are designed to lengthen muscle under tension.
Intensity and novelty:
High-intensity workouts often lead to muscle soreness and stiffness. Even if you engage in new exercises you will also feel stiffness in your muscles.
Inflammation:
Inflammation is triggered by muscle damage which leads to sensation of soreness and swelling.
Strategies for treating muscle soreness
Here is a list of immediate strategies that will help to treat muscle soreness.
Rest and recovery:
Muscle soreness means your muscles are adapting to the new changes and the stimuli. Your body needs rest which is a crucial aspect of treating muscle soreness. Don’t target your sore muscles instead do some stretching that will help with the soreness and ensure to take proper rest so muscles can recover themselves. Take adequate sleep of 7-9 hours to prioritize your recovery.
Cold therapy:
Cold therapy includes applying ice or cold packs to sore muscles. The therapy helps to reduce inflammation which is triggered by muscle damage. You can get temporary relief from pain by numbing the area where you are feeling sore. If you want to use cold therapy you should apply it within 24 hours of exercise for effective results.
Compression:
Compression garments are used for faster recovery because they can help reduce swelling and improve circulation.
Elevation:
If you are feeling sore in your legs and arms, elevating them can help to reduce swelling by encouraging fluid drainage away from affected areas.
Gentle stretching:
Gentle stretching can help to reduce swelling and recover your sore muscles because it improves blood circulation.
Long-term treatment and management
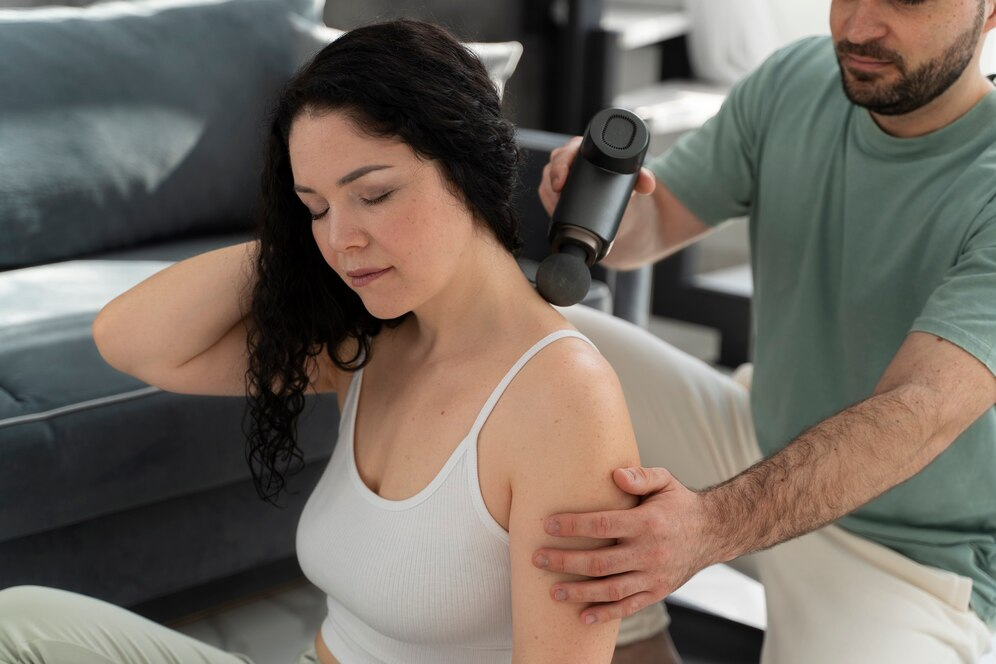

When you engage in intense workouts on a regular basis you will experience muscle soreness long-term. You need to opt for strategies that will help to better your sore muscles by treating and managing them in the long-run.
Active recovery:
Ensure to incorporate low-intensity exercises in your workout routine for active recovery. Activities like walking, swimming and cycling can help improve blood circulation that will help alleviate sore muscles. A regulated blood circulation is necessary to heal muscle soreness because it helps to deliver nutrients and oxygen to the muscles.
Massage therapy:
Opt for massage therapy to relieve muscle soreness and stiffness. Massage can help to improve blood circulation and promote relaxation. Deep tissue massage or sports massage are excellent options to opt for as a massage therapy to heal muscle soreness.
Hydration:
Staying well hydrated is crucial in muscle gain or for any other fitness goal. In this case, water helps to flush out toxins and also reduce inflammation which is triggered by muscle soreness. Water also helps with nutrient absorption and its transportation.
Nutritional support:
Proper nutrition for muscle building is crucial and it also supports muscle recovery. Protein is your go-to micronutrients in the journey of muscle building. Protein being the building block of your muscle tissues helps in repairing them. Yes, you have to increase the intake of protein but also keep your meals balanced and add complex carbohydrates and healthy fats in your diet. Include healthy food sources like fruits and vegetables which are also a great source of antioxidants which help to reduce inflammation and support recovery.
Sleep:
Quality sleep is essential to give rest to your body for allowing your body to repair muscle tissues. Aim to get 7-9 hours of sleep to promote recovery of your muscles. Proper sleep will help to reduce muscle soreness and stiffness.
Supplements:
Do not compromise on the consumption of various minerals essential for muscle recovery and your overall health. Include food sources but along with that you can also consume supplements to aid muscle recovery.
Supplements like branch-chain amino acids BCAAs, omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, and magnesium should be your top priority.
Preventive strategies

People who have started muscle gain journey would experience muscle soreness whether mild or severe. You can totally avoid it but you surely can implement some of the preventive measures to reduce the severity of soreness.
Warm-up:
Before beginning your workout sessions ensure to do a proper warm-up to increase the blood flow to your muscles. This helps them to prepare for the upcoming activities you are going to perform. Stretching, light cardio and mobility exercises can help reduce the risk of injury and soreness.
Gradual progression:
Start with small steps. Do not include heavy workouts in the beginning and tend to increase the intensity of your workout slowly and gradually. Let your body first adjust to the changes your muscles go through so the likelihood of severe soreness can be reduced.
Cool down and stretch:
After a workout session make sure to cool down with light activity and stretching. Post-workout activity helps to bring back your heart rate to normal which reduces muscle stiffness.
Consistent training:
Consistency is the key to get effective results. Muscle soreness is common when building muscles or carrying out any exercise. Keep in mind to be consistent with your exercise routine so your muscles get adapted to stress over time. Consistency will help you to build resilience during soreness.
Cross training:
Do not stick to one exercise. There are many exercises that align with your health goals. In every session try to incorporate various types of exercises which can also help you to avoid overloading specific muscle groups.
Listen to your body:
You need to pay attention and listen to your body’s cues. Pay attention to how your body feels during and after exercise. If you are consistently experiencing soreness it might be a sign that you need to adjust your workout routine. The adjustment could come in the form of change in exercises, frequency of sets and reps or changing the intensity of your workout.
When to seek medical help?

Muscle soreness is common during muscle gain journey but you sometimes might need immediate medical help in the following cases:
Severe pain:
If you are experiencing severe pain even after getting proper rest and you don’t see any improvement you should seek medical attention because it could be a serious injury.
Swelling and bruising:
Muscle building leads to muscle stiffness and soreness but not major swelling or bruising. So, if you experience or witness swelling or bruising in your muscles, you should ask for medical help.
Persistent soreness:
Muscle soreness usually lasts for a week but if you are experiencing it for more than a week it might need medical attention.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does muscle soreness take to heal?
Ans. Muscle soreness usually lasts up to 2-5 days and a maximum of 7 days.
Can I workout with sore muscles?
Ans. You can workout with sore muscles as long as you are not putting much stress on your muscles.
Should I skip workout if I am sore?
Ans. If you are sore you should focus on active recovery which means to indulge in movement even if you feel sore to prevent stiffness. Do not indulge in workout if you have severe pains or any minor injury.




